Modalities
Blading
Graston
Technique
Blades are a popular treatment tool for myofascial restriction in all kinds of soft tissue conditions, whether they are chronic, acute or post-surgical.
What is blading –
Graston Technique
/ IASTM?
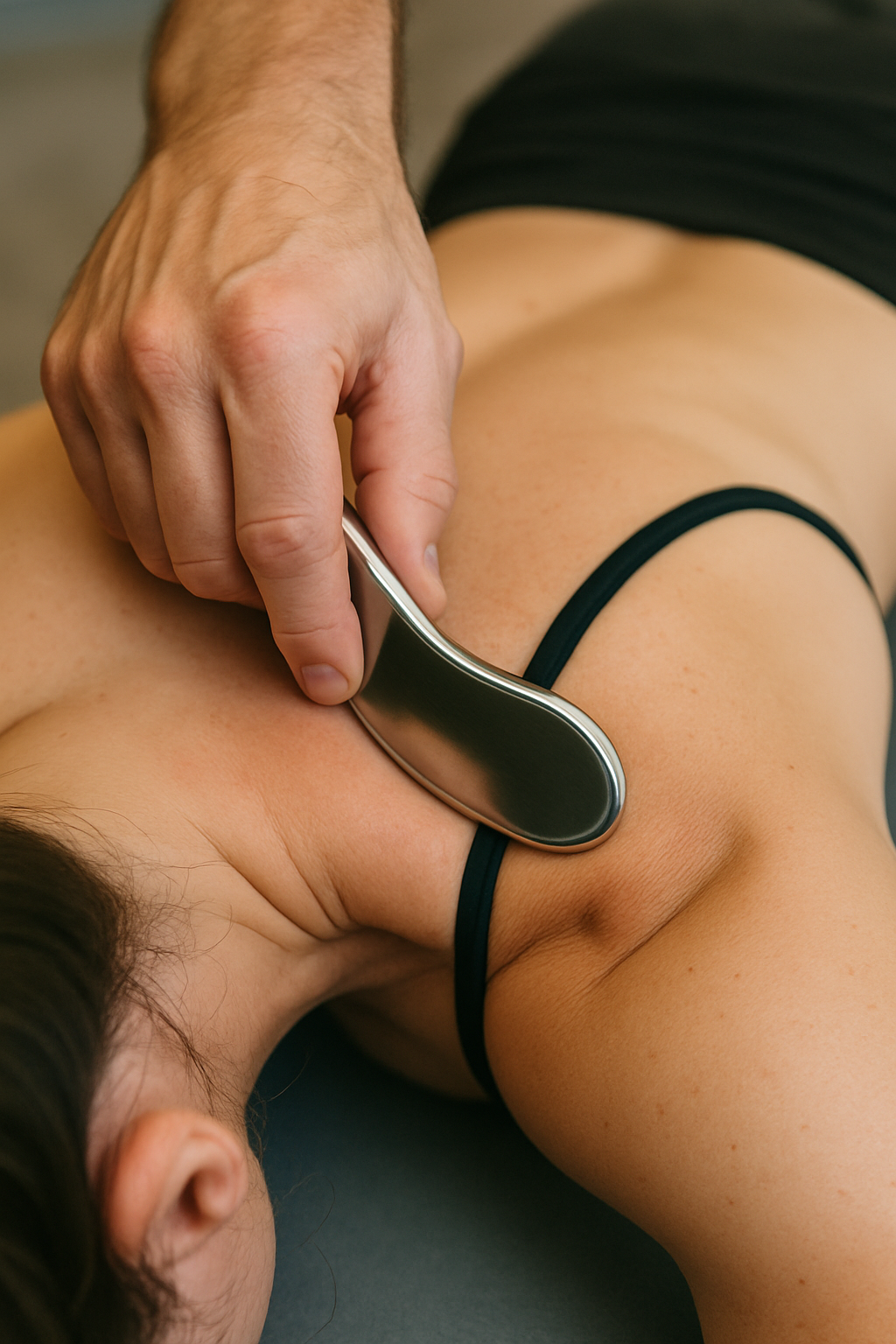
Blading refers to a type of soft tissue therapy that uses a smooth, hard tool — usually stainless steel — to scrape or glide over the skin and underlying muscles, fascia, and tendons.
It’s formally known as:
Instrument-Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization – IASTM for short.
“Graston Technique” is one of the most popular branded methods, but others exist too.
Practitioners use the edge of the tool to detect and treat areas of scar tissue, adhesions, or restricted fascia. It’s sometimes called scraping, though the word “scraping” sounds harsher than what it actually is.
How does it work?
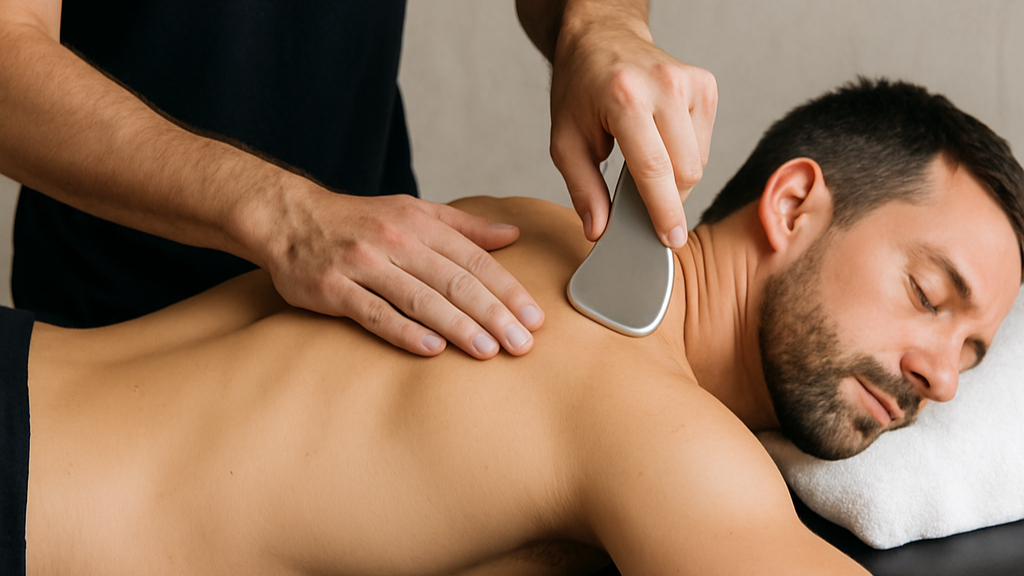
The therapist applies a lubricant and then moves the tool along the skin with firm, controlled pressure.
The pressure and shear forces help break up adhesions or scar tissue in the soft tissue.
This may stimulate a localized inflammatory response that promotes healing, increases blood flow, and improves mobility.
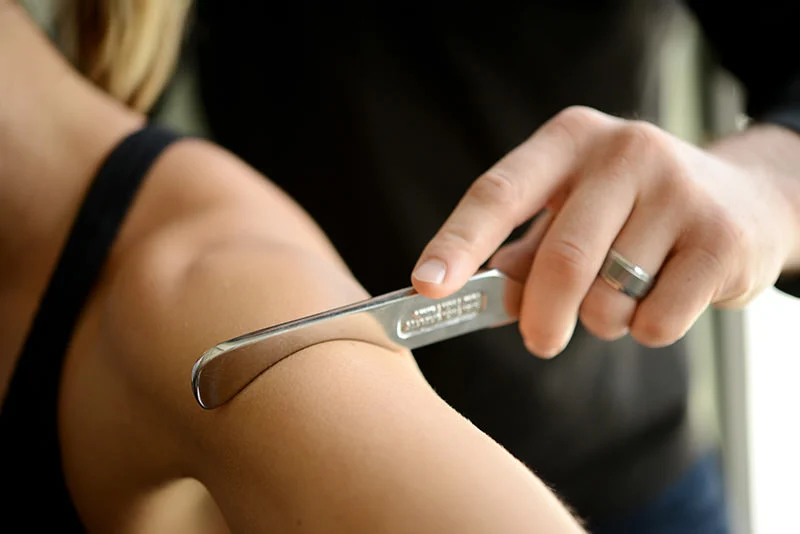

What conditions is it used for?
✅ Tendinitis / tendinopathy (e.g., tennis elbow, Achilles)
✅ Plantar fasciitis
✅ Muscle strains
✅ IT band syndrome
✅ Carpal tunnel syndrome
✅ Post-surgical or post-injury scar tissue
✅ Chronic muscle tightness
CLAIMED BENEFITS
- Breaks down scar tissue & adhesions
Helps remodel fibrotic tissue after injuries (like sprains, tendinopathy, or surgery). - Improves range of motion
By freeing up restricted fascia and tissue, joints and muscles can move more freely. - Reduces pain & stiffness
May decrease pain by improving tissue quality and circulation.
- Speeds up recovery & healing
The controlled microtrauma may trigger healing processes and bring nutrients to the area. - Enhances athletic performance
Many athletes use it preventively to keep soft tissue healthy and mobile.
Notes & Precautions:
- It may leave temporary redness, bruising, or soreness — that’s normal.
- Should only be performed by a trained professional.
- Not recommended for people with certain conditions (e.g., blood clotting disorders, open wounds, infections) without medical advice.